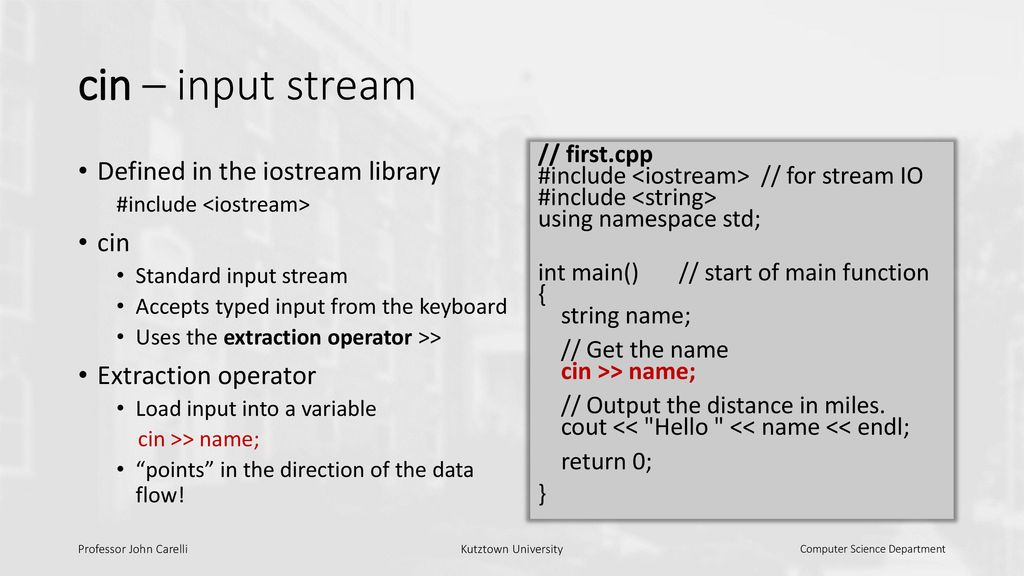
In most program environments, the standard input by default is the keyboard, and the C++ stream object defined to access it is cin. cin is an instance of iostream class
For formatted input operations, cin is used together with the extraction operator, which is written as >> (i.e., two "greater than" signs). This operator is then followed by the variable where the extracted data is stored. For example:
int age;
//declares a variable of type int called age
cin >> age;
//extracts a value to be stored in it
This operation makes the program wait for input from cin; generally, this means that the program will wait for the user to enter some sequence with the keyboard.
Extractions on cin can also be chained to request more than one datum in a single statement:
cin >> a >> b;
This is equivalent to:
cin >> a;
cin >> b;
In both cases, the user is expected to introduce two values, one for variable a, and another for variable b. Any kind of space is used to separate two consecutive input operations; this may either be a space, a tab, or a new-line character.
5.3 cerr (error stream) NEXT >>